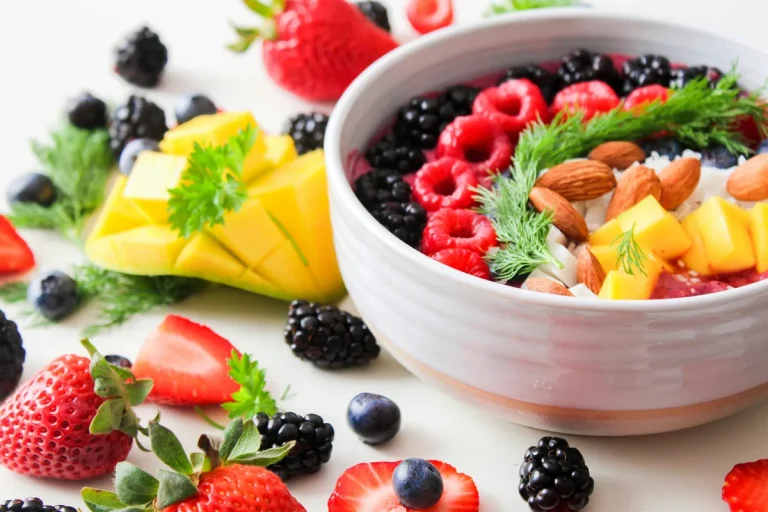
Nutrient density refers to how many vitamins, minerals, and beneficial compounds a food contains relative to its calorie content.
- Examples of nutrient-dense foods: leafy greens, berries, eggs, legumes, salmon
- These foods provide more nutritional value per bite, helping you meet your needs without excess calories
- Contrast this with empty-calorie foods like soda or candy, which offer energy but little else
Choosing nutrient-dense foods supports energy, immunity, and long-term health — without relying on restriction.